使用深度学习技术进行异常检测
识别数据中的异常(或异常值)对于来自科学和技术各个领域的科学家和工程师来说都是一个挑战。尽管检测异常(可疑对象与主数据集不相似)已经处理了很长时间,并且最早的算法是上个世纪60年代开发的,但是在该领域,人们仍然面临着许多未解决的问题和难题,例如咨询,银行计分,信息安全,金融交易和医疗保健。在过去的几年中,随着深度学习算法的迅速发展,针对各种类型的研究数据(例如图像,闭路电视摄像机的记录,表格数据(关于金融交易)等)提出了许多解决此问题的现代方法。
- Deep Anomaly Detection (DAD) - :
: . . - , ,
:
:
: , , , ( - )
:
precision / ( )
[2] G. Pang .
:
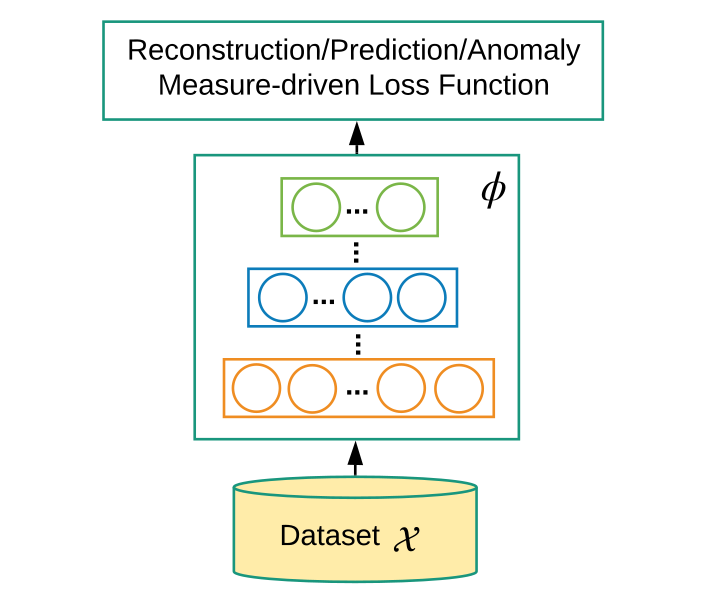
Deep learning for feature extraction - , ( ), . DAD.
.2 . φ(·) : X→ Z Z, .
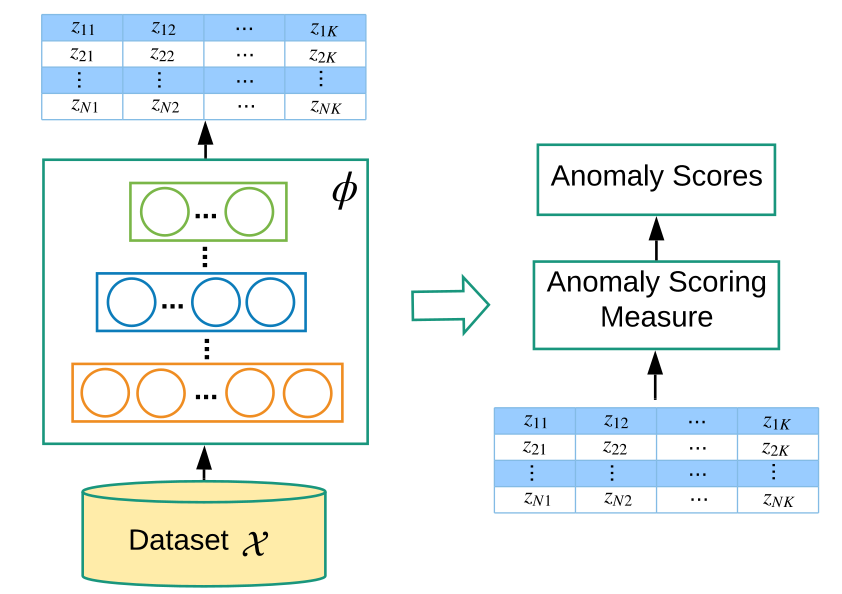
Learning feature representation of normality - φ(·) : X→ Z , , Z .
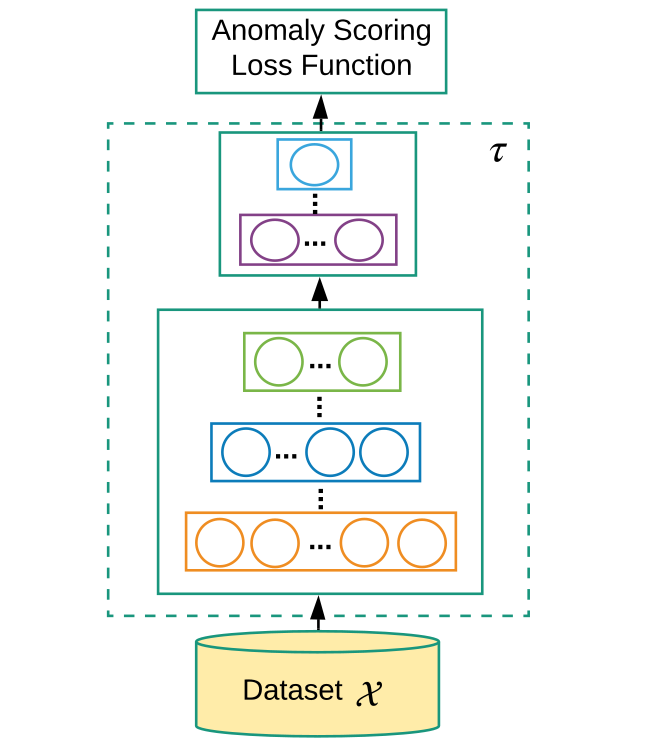
End-to-end anomaly score learning - end-to-end , anomaly score.
, .
Deep learning for feature extraction
. , PCA (principal component analysis) [3] random projection [4], , . MLP, , NNs , RNNs ().
, anomaly score .
Learning feature representation of normality
.1 .
Generic Normality Feature Learning. . , .
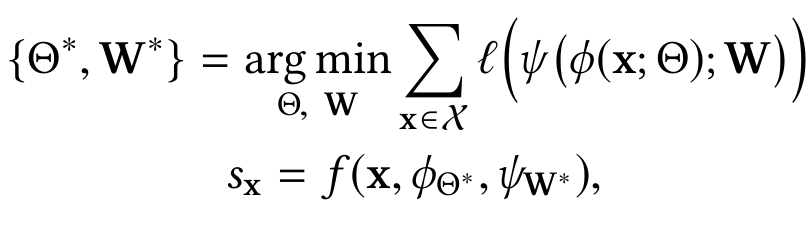
ψ - , l - , ψ, φ ( ), f - .
:
DAD , , . [5]
- , , , .
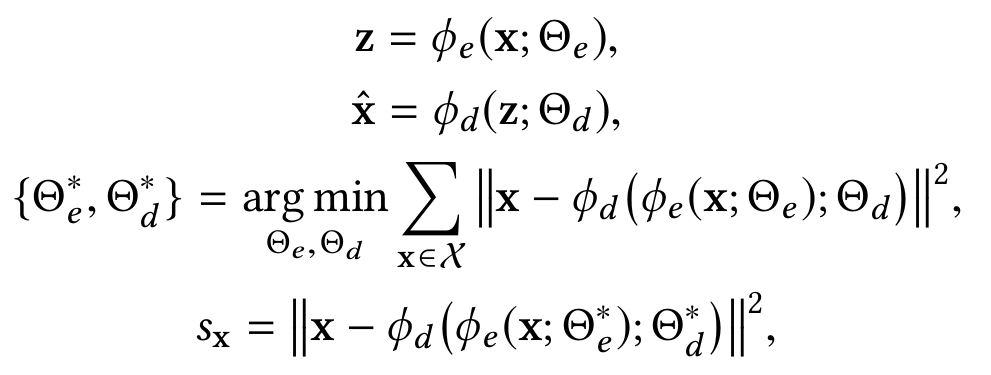
φ_e (.) - , , φ_d (.) - , . s_x (data reconstruction error) .
Generative Adversarial Networks
GANs - , , ( G) , ( D) .
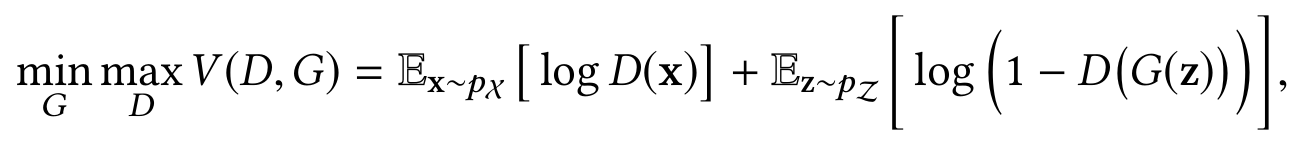
G D - .
DAD , . , , . AnoGAN [6].
Predictability Modeling. .

x̂_(t +1) = ψ (φ (x1 , x2 , · · · , xt ; Θ); W),
l_pred l_adv - , .
, , . . [7]
Self-supervised Classification. , ( - (n - 1) , - , ). . , .
Anomaly Measure-dependent Feature Learning.
φ(·) : X→ Z, .
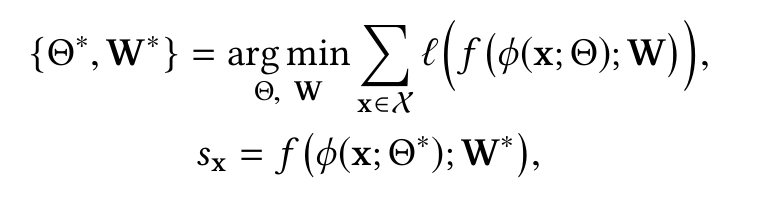
l - .
:
Distance-based Measure. , : DB outliers [8], k-nearest neighbor distance [9] . - , .
One-class Classification-based Measure. , , , . one-class SVM [10], Support Vector Data Description (SVDD) [11].
Clustering-based Measure. , , [12].
End-to-end anomaly score learning
, anomaly score.
:
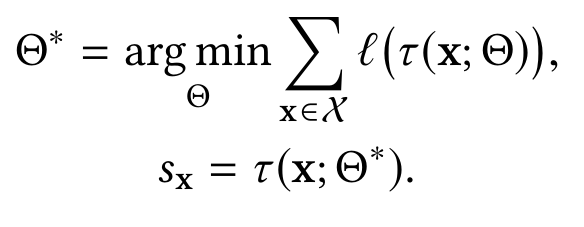
τ (x; Θ) : X→ R , .
Ranking Models. end-to-end . , . Self-trained deep ordinal regression model [13].
Prior-driven Models. - the Bayesian inverse RL-based sequential anomaly detection. - , . [14].
Softmax Models. , . , .
Deviation Networks (end-to-end pipeline) [1]
, G. Pang , . .5 .
function φ - anomaly scoring network, . Reference score generator - , ( ). ( φ(x; Θ) μ_R) deviation loss function L, anomaly scoring network , , .
deviation loss function
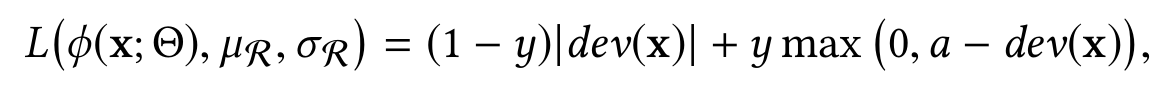

y = 1, , y = 0 . , anomaly score , φ(x; Θ), dev(x) , , "a" ( ). .
, , . SOTA-. end-to-end .
[1] Deep Anomaly Detection with Deviation Networks. G. Pang
[2] Deep Learning for Anomaly Detection: A Review. G. Pang
[3] Emmanuel J Candès, Xiaodong Li, Yi Ma, and John Wright. 2011. Robust principal component analysis?
[4] Ping Li, Trevor J Hastie, and Kenneth W Church. 2006. Very sparse random projections.
[5] Alireza Makhzani and Brendan Frey. 2014. K-sparse autoencoders. In ICLR.
[6] Thomas Schlegl, Philipp Seeböck, Sebastian M Waldstein, Ursula Schmidt-Erfurth, and Georg Langs. 2017. Unsupervised anomaly detection with generative adversarial networks to guide marker discovery.
[7] Wen Liu, Weixin Luo, Dongze Lian, and Shenghua Gao. 2018. Future frame prediction for anomaly detection–a new baseline.
[8] Edwin M Knorr and Raymond T Ng. 1999. Finding intensional knowledge of distance-based outliers.[9] Fabrizio Angiulli and Clara Pizzuti. 2002. Fast outlier detection in high dimensional spaces.
[10] Bernhard Schölkopf, John C Platt, John Shawe-Taylor, Alex J Smola, and Robert C Williamson. 2001. Estimating the support of a high-dimensional distribution.
[11] David MJ Tax and Robert PW Duin. 2004. Support vector data description.
[12] Mathilde Caron, Piotr Bojanowski, Armand Joulin, and Matthijs Douze. 2018. Deep clustering for unsupervised learning of visual features.
[13] Guansong Pang, Cheng Yan, Chunhua Shen, Anton van den Hengel, and Xiao Bai. 2020. Self-trained Deep Ordinal Regression for End-to-End Video Anomaly Detection.
[14] Andrew Y Ng和Stuart J Russell。2000。反强化学习算法。