将获得的信息存储在缓存中是不切实际的;必须使用数据库。
在本文中,我将考虑:
- 创建一个简单的SQLite数据库;
- 使用Python编写信息;
- 读取数据并转换为DataFrame格式;
- 根据数据库数据解析更新。

数据库要求
项目数据库的主要要求是存储数据并能够快速检索它。
我们的数据库不是必需的:
- 限制对方案的访问,因为 只有用户才能通过解析进行访问;
- 保持访问24/7,因为 分析所需的数据提取是可接受的;
- 创建程序,自 所有计算将在python中完成。
因此,项目可以在SQLite中使用简单的数据库。您可以将其作为文件存储在硬盘驱动器,USB闪存驱动器或云驱动器上,以从其他设备进行访问。
通过python使用SQLite的功能
要通过python使用SQLite,我们使用sqlite3库。
我们使用一个简单的命令连接到数据库:
sqlite3.connect( )如果文件丢失,将创建一个新的数据库。
数据库查询执行如下:
conn = sqlite3.connect( )
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute()
df = cur.fetchall()
当由于请求而要从数据库获取数据时,将执行cur.fetchall()。
在将数据写入数据库结束时,请不要忘记结束事务:
conn.commit()
并且在使用数据库结束时,请不要忘记关闭它:
conn.close()
否则,底座将被锁定以进行书写或打开。
创建表是标准的:
CREATE TABLE t1 (1 , 2 ...)
或更通用的选项(如果缺少的话)创建表:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS t1 (1 , 2 ...)我们将数据写入表,避免重复:
INSERT OR IGNORE INTO t1 (1, 2, ...) VALUES(1, 2, ...)更新数据:
UPDATE t1 SET 1 = 1 WHERE 2 = 2为了更方便地使用SQLite,可以将SQLite Manager或DB Browser用于SQLite。
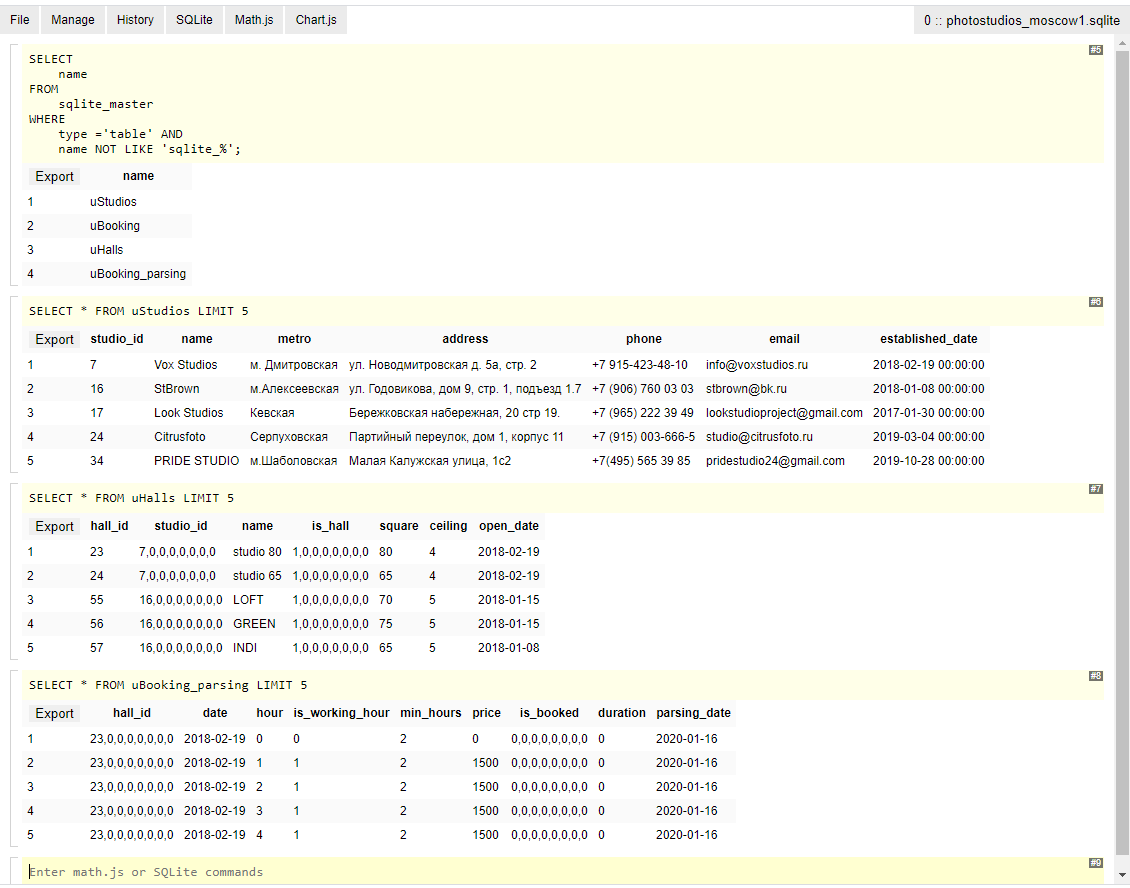
第一个程序是浏览器的扩展,看起来像是请求行和响应块的交替:
第二个程序是成熟的桌面应用程序:
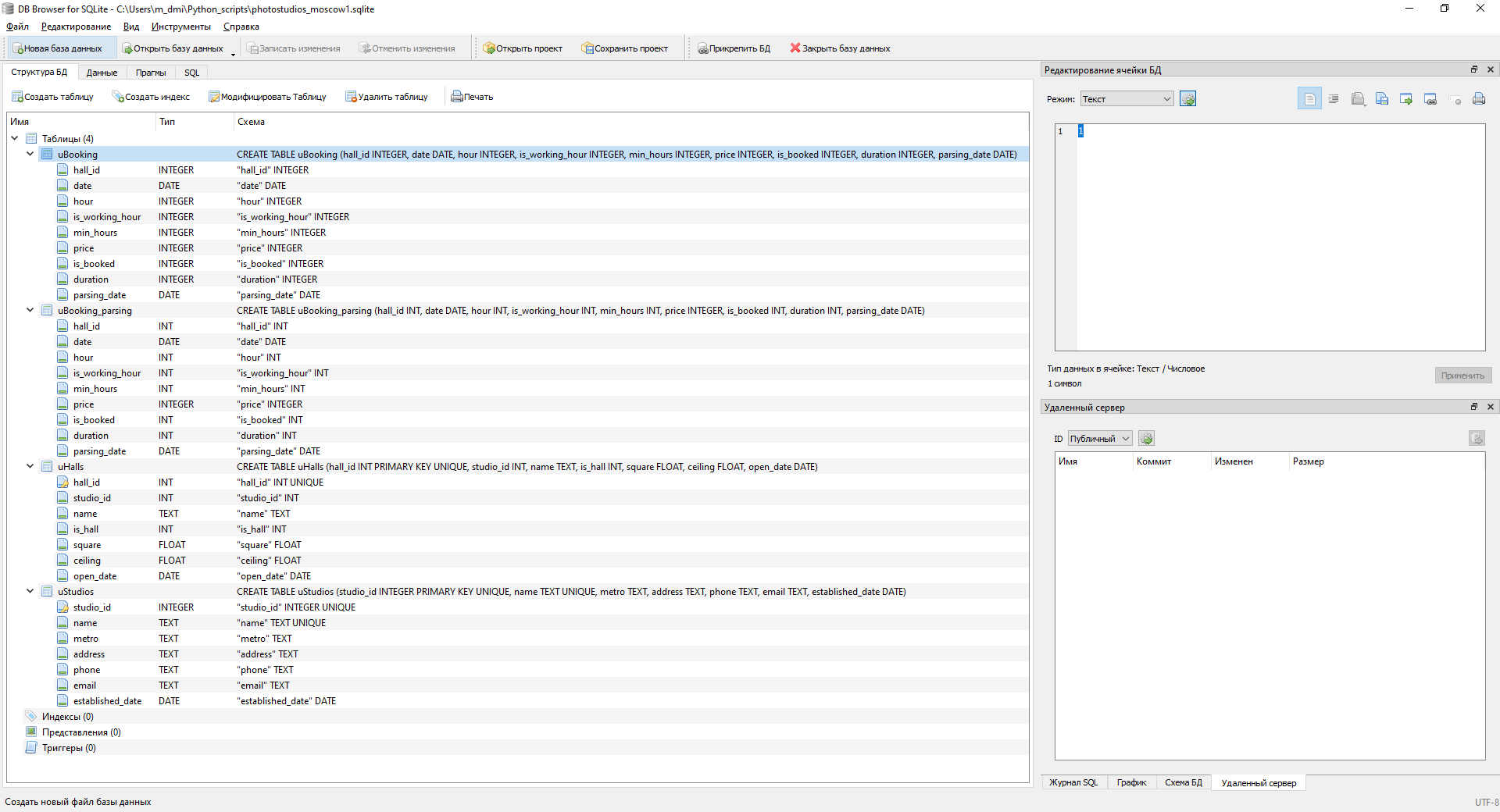
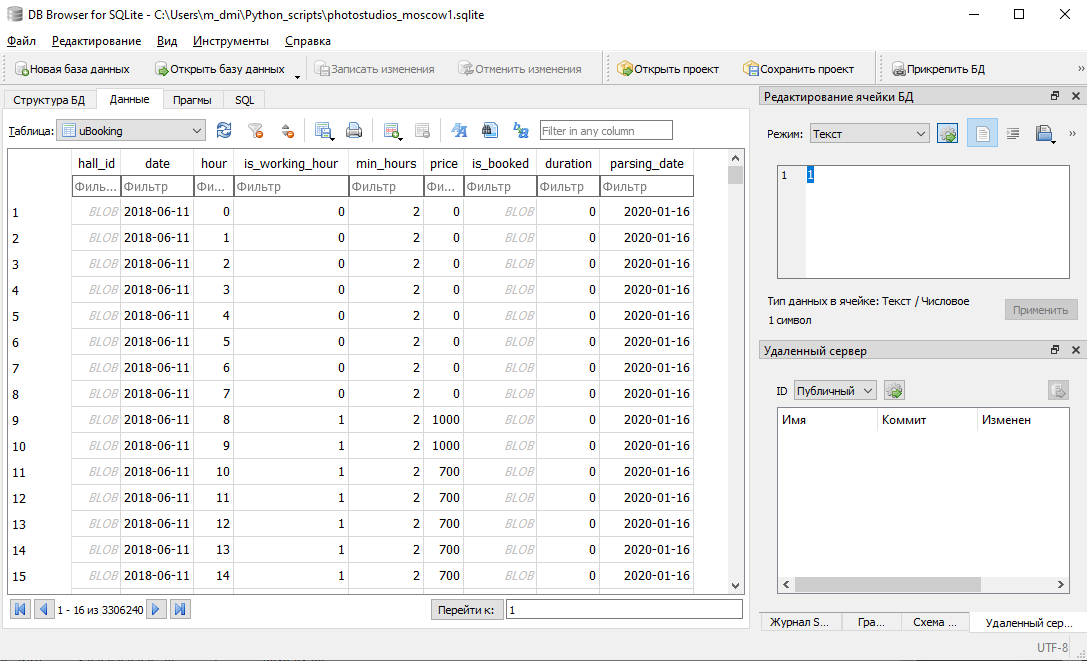
数据库结构
该数据库将包含4个表:工作室,大厅,2个预订表。
上载的预订数据包含有关未来期间的信息,这些信息可能会随着新的分析而改变。覆盖数据是不希望的(例如,可以使用它们来计算预订时的天/小时)。因此,原始解析数据需要一个预订表,而最新的相关表则需要另一个预订表。
我们创建表:
def create_tables(conn, table = 'all'):
cur = conn.cursor()
if (table == 'all') or (table == 'uStudios'):
cur.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS uStudios
(studio_id INT PRIMARY KEY UNIQUE,
name TEXT UNIQUE,
metro TEXT,
address TEXT,
phone TEXT,
email TEXT,
established_date DATE)
''')
print('Table uStudios is created.')
if (table == 'all') or (table == 'uHalls'):
cur.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS uHalls
(hall_id INT PRIMARY KEY UNIQUE,
studio_id INT,
name TEXT,
is_hall INT,
square FLOAT,
ceiling FLOAT,
open_date DATE)
''')
print('Table uHalls is created.')
if (table == 'all') or (table == 'uBooking_parsing'):
cur.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS uBooking_parsing
(hall_id INT,
date DATE,
hour INT,
is_working_hour INT,
min_hours INT,
price INTEGER,
is_booked INT,
duration INT,
parsing_date DATE)
''')
print ('Table uBooking_parsing is created.')
if (table == 'all') or (table == 'uBooking'):
cur.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS uBooking
(hall_id INT,
date DATE,
hour INT,
is_working_hour INT,
min_hours INT,
price INTEGER,
is_booked INT,
duration INT,
parsing_date DATE)
''')
print ('Table uBooking is created.')
table参数设置要创建的表的名称。默认情况下创建所有内容。
在表格的字段中,您可以看到尚未解析的数据(工作室开放日期,大厅开放日期)稍后我将描述这些字段的计算。
与数据库的交互
让我们创建6个与数据库交互的过程:
- 将摄影棚清单写入数据库;
- 从数据库上传照相馆清单;
- 记录大厅清单;
- 卸载大厅清单;
- 上传预订数据;
- 记录预订数据。
1.将摄影棚清单写入数据库
在该过程的入口,我们以DataFrame的形式传递用于连接数据库和表的参数。我们逐行写入数据,在循环中遍历所有行。python中用于此操作的字符串数据的有用属性是“?” 之后指定的元组的元素。
记录照相馆清单的步骤如下:
def studios_to_db(conn, studio_list):
cur = conn.cursor()
for i in studio_list.index:
cur.execute('INSERT OR IGNORE INTO uStudios (studio_id, name, metro, address, phone, email) VALUES(?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)',
(i,
studio_list.loc[i, 'name'],
studio_list.loc[i, 'metro'],
studio_list.loc[i, 'address'],
studio_list.loc[i, 'phone'],
studio_list.loc[i, 'email']))2.从数据库上传照相馆列表
在该过程的入口,我们传递用于连接数据库的参数。我们执行选择查询,拦截卸载的数据并将其写入DataFrame。我们以日期格式转换照相馆的成立日期。
整个过程如下:
def db_to_studios(conn):
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('SELECT * FROM uStudios')
studios = pd.DataFrame(cur.fetchall()
, columns=['studio_id', 'name', 'metro', 'address', 'phone', 'email', 'established_date']
).set_index('studio_id')
studios['established_date'] = pd.to_datetime(studios['established_date'])
return studios3.将大厅列表写入数据库
该过程类似于记录摄影棚的列表:我们传输连接参数和大厅表,然后将数据逐行写入数据库。
在数据库中记录大厅列表的过程
def halls_to_db(conn, halls):
cur = conn.cursor()
for i in halls.index:
cur.execute('INSERT OR IGNORE INTO uHalls (hall_id, studio_id, name, is_hall, square, ceiling) VALUES(?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)',
(i,
halls.loc[i, 'studio_id'],
halls.loc[i, 'name'],
halls.loc[i, 'is_hall'],
halls.loc[i, 'square'],
halls.loc[i, 'ceiling']))4.从数据库中卸载大厅列表
该过程类似于卸载照相馆列表:传输连接参数,选择请求,拦截,写入DataFrame,将大厅的开放日期转换为日期格式。
唯一的区别是:工作室ID和大厅标志以字节形式记录。我们通过函数返回值:
int.from_bytes(, 'little')
卸载大厅列表的过程如下:
def db_to_halls(conn):
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('SELECT * FROM uHalls')
halls = pd.DataFrame(cur.fetchall(), columns=['hall_id', 'studio_id', 'name', 'is_hall', 'square', 'ceiling', 'open_date']).set_index('hall_id')
for i in halls.index:
halls.loc[i, 'studio_id'] = int.from_bytes(halls.loc[i, 'studio_id'], 'little')
halls.loc[i, 'is_hall'] = int.from_bytes(halls.loc[i, 'is_hall'], 'little')
halls['open_date'] = pd.to_datetime(halls['open_date'])
return halls5.从数据库上传预订信息
我们将数据库连接参数和解析参数传递给该过程,以显示我们正在从哪个预订表中请求信息:0-来自实际(默认情况下),1-来自解析表。接下来,我们执行一个选择请求,将其拦截,并将其转换为DataFrame。日期转换为日期格式,数字从字节格式转换为数字格式。
上传预订信息的过程:
def db_to_booking(conn, parsing = 0):
cur = conn.cursor()
if parsing == 1:
cur.execute('SELECT * FROM uBooking_parsing')
else:
cur.execute('SELECT * FROM uBooking')
booking = pd.DataFrame(cur.fetchall(), columns=['hall_id',
'date', 'hour',
'is_working_hour',
'min_hours',
'price',
'is_booked',
'duration',
'parsing_date'])
booking['hall_id'] = [int.from_bytes(x, 'little') if not isinstance(x, int) else x for x in booking['hall_id']]
booking['is_booked'] = [int.from_bytes(x, 'little') if not isinstance(x, int) else x for x in booking['is_booked']]
booking['date'] = pd.DataFrame(booking['date'])
booking['parsing_date'] = pd.DataFrame(booking['parsing_date'])
return booking6.将预订信息写入数据库
与数据库交互的最复杂功能,因为 它启动对预订数据的解析。在入口处,我们将连接数据库的参数和必须更新的大厅ID列表传递给该过程。
要确定最新数据的最新日期,
从数据库中请求每个大厅ID的最新解析日期:
parsing_date = db_to_booking(conn, parsing = 1).groupby('hall_id').agg(np.max)['parsing_date']我们使用循环遍历每个大厅ID。
在每个大厅ID中,我们要做的第一件事是定义
过去要解析的周数:
try:
last_day_str = parsing_date[id]
last_day = datetime.datetime.strptime(last_day_str, '%Y-%m-%d')
delta_days = (datetime.datetime.now() - last_day).days
weeks_ago = delta_days // 7
except:
last_day_str = '2010-01-01'
last_day = datetime.datetime.strptime(last_day_str, '%Y-%m-%d')
weeks_ago = 500如果大厅ID在数据库中,则我们进行计算。如果不是,那么我们将解析过去500周,或者在两个月没有预订的情况下停止解析(限制已在上一篇文章中进行了描述)。
然后我们执行解析过程:
d = get_past_booking(id, weeks_ago = weeks_ago)
d.update(get_future_booking(id))
book = hall_booking(d)首先,我们将过去的预订信息解析为实际数据,然后从未来(长达2个月,没有记录)进行解析,最后,我们将数据从json格式传输到DataFrame。
在最后阶段,我们将预订大厅的数据写入数据库并完成交易。
将预订信息记录到数据库中的过程如下:
def booking_to_db(conn, halls_id):
cur = conn.cursor()
cur_date = pd.Timestamp(datetime.date.today())
parsing_date = db_to_booking(conn, parsing = 1).groupby('hall_id').agg(np.max)['parsing_date']
for id in halls_id:
#download last parsing_date from DataBase
try:
last_day_str = parsing_date[id]
last_day = datetime.datetime.strptime(last_day_str, '%Y-%m-%d')
delta_days = (datetime.datetime.now() - last_day).days
weeks_ago = delta_days // 7
except:
last_day_str = '2010-01-01'
last_day = datetime.datetime.strptime(last_day_str, '%Y-%m-%d')
weeks_ago = 500
d = get_past_booking(id, weeks_ago = weeks_ago)
d.update(get_future_booking(id))
book = hall_booking(d)
for i in list(range(len(book))):#book.index:
cur.execute('INSERT OR IGNORE INTO uBooking_parsing (hall_id, date, hour, is_working_hour, min_hours, price, is_booked, duration, parsing_date) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?)',
(book.iloc[i]['hall_id'],
book.iloc[i]['date'].date().isoformat(),
book.iloc[i]['hour'],
book.iloc[i]['is_working_hour'],
book.iloc[i]['min_hours'],
book.iloc[i]['price'],
book.iloc[i]['is_booked'],
book.iloc[i]['duration'],
cur_date.date().isoformat()))
conn.commit()
print('hall_id ' + str(id) + ' added. ' + str(list(halls_id).index(id) + 1) + ' from ' + str(len(halls_id)))更新工作室和大厅的开放日
休息室的开放日期是休息室的最早预订日期。
照相馆的开幕日期是照相馆大厅开幕的最早日期。
基于这种逻辑,
我们从数据库中卸载每个房间的最早预订日期
halls = db_to_booking(conn).groupby('hall_id').agg(min)['date']
然后,我们逐行更新大厅开放的数据:
for i in list(range(len(halls))):
cur.execute('''UPDATE uHalls SET open_date = '{1}' WHERE hall_id = {0}'''
.format(halls.index[i], str(halls.iloc[i])))我们以相同的方式更新照相馆的开业数据:我们从数据库中下载展馆开幕日期的数据,计算每个照相馆的最小日期,然后重写照相馆的开业日期。
更新开放日期的步骤:
def update_open_dates(conn):
cur = conn.cursor()
#update open date in uHalls
halls = db_to_booking(conn).groupby('hall_id').agg(min)['date']
for i in list(range(len(halls))):
cur.execute('''UPDATE uHalls SET open_date = '{1}' WHERE hall_id = {0}'''
.format(halls.index[i], str(halls.iloc[i])))
#update open date in uStudios
studios = db_to_halls(conn)
studios['open_date'] = pd.to_datetime(studios['open_date'])
studios = studios.groupby('studio_id').agg(min)['open_date']
for i in list(range(len(studios))):
cur.execute('''UPDATE uStudios SET established_date = '{1}' WHERE studio_id = {0}'''
.format(studios.index[i], str(studios.iloc[i])))
conn.commit()解析更新
我们将结合 本过程中的所有过程以及本过程中的上一篇文章。它可以在第一次解析和更新数据时启动。
该过程如下所示:
def update_parsing(directory = './/', is_manual = 0):
start_time = time.time()
#is DataBase exists?
if not os.path.exists(directory + 'photostudios_moscow1.sqlite'):
if is_manual == 1:
print('Data base is not exists. Do you want to create DataBase (y/n)? ')
answer = input().lower()
else:
answer == 'y'
if answer == 'y':
conn = sqlite3.connect(directory + 'photostudios_moscow1.sqlite')
conn.close()
print('DataBase is created')
elif answer != 'n':
print('Error in input!')
return list()
print('DataBase is exists')
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
start_time = time.time()
#connect to DataBase
conn = sqlite3.connect(directory + 'photostudios_moscow1.sqlite')
cur = conn.cursor()
#has DataBase 4 tables?
tables = [x[0] for x in list(cur.execute('SELECT name FROM sqlite_master WHERE type="table"'))]
if not ('uStudios' in tables) & ('uHalls' in tables) & ('uBooking_parsing' in tables) & ('uBooking' in tables):
if is_manual == 1:
print('Do you want to create missing tables (y/n)? ')
answer = input().lower()
else:
answer = 'y'
if anwer == 'y':
if not ('uStudios' in tables):
create_tables(conn, table = 'uStudios')
if not ('uHalls' in tables):
create_tables(conn, table = 'uHalls')
if not ('uBooking_parsing' in tables):
create_tables(conn, table = 'uBooking_parsing')
if not ('uBooking' in tables):
create_tables(conn, table = 'uBooking')
elif answer != 'n':
print('Error in input!')
return list()
conn.commit()
print(str(tables) + ' are exist in DataBase')
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
start_time = time.time()
#update uStudios
studios = studio_list()
new_studios = studios[[x not in list(db_to_studios(conn).index) for x in list(studios.index)]]
if len(new_studios) > 0:
print(str(len(new_studios)) + ' new studios detected: \n' + str(list(new_studios['name'])))
studios_to_db(conn, new_studios)
conn.commit()
print('Studio list update was successful')
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
start_time = time.time()
#update uHalls
halls = hall_list(list(studios.index)).sort_index()
new_halls = halls[[x not in list(db_to_halls(conn).index) for x in list(halls.index)]]
if len(new_halls) > 0:
halls_to_db(conn, new_halls)
conn.commit()
print('Halls list update was successful')
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
start_time = time.time()
#update uBooking_parsing
booking_to_db(conn, halls.index)
conn.commit()
print('Booking_parsing update was successful')
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
start_time = time.time()
#update uBooking from uBooking_parsing
cur.execute('DELETE FROM uBooking')
cur.execute('''
insert into uBooking (hall_id, date, hour, is_working_hour, min_hours, price, is_booked, duration, parsing_date)
select hall_id, date, hour, is_working_hour, min_hours, price, is_booked, duration, parsing_date
from
(
select *, row_number() over(partition by hall_id, date, hour order by parsing_date desc) rn
from uBooking_parsing
) t
where rn = 1
''')
conn.commit()
print('Booking update was successful')
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
start_time = time.time()
update_open_dates(conn)
conn.commit()
print('Open date update was successful')
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
conn.close()
让我们按顺序分析她的工作。
在该过程的入口处,我们传递了两个参数:从中获取数据库或在其上安装数据库的文件夹的地址(默认情况下,我们使用python文档获取该文件夹),以及可选的is_manual参数,如果将其设置为“ 1”,则将要求在其中创建数据库或表在他们不在的情况下。
. , :
if not os.path.exists(directory + 'photostudios_moscow1.sqlite'):
if is_manual == 1:
print('Data base is not exists. Do you want to create DataBase (y/n)? ')
answer = input().lower()
else:
answer == 'y'
if answer == 'y':
conn = sqlite3.connect(directory + 'photostudios_moscow1.sqlite')
conn.close()
print('DataBase is created')
elif answer != 'n':
print('Error in input!')
return list()
:
conn = sqlite3.connect(directory + 'photostudios_moscow1.sqlite')
cur = conn.cursor()
, . , . :
tables = [x[0] for x in list(cur.execute('SELECT name FROM sqlite_master WHERE type="table"'))]
if not ('uStudios' in tables) & ('uHalls' in tables) & ('uBooking_parsing' in tables) & ('uBooking' in tables):
if is_manual == 1:
print('Do you want to create missing tables (y/n)? ')
answer = input().lower()
else:
answer = 'y'
if anwer == 'y':
if not ('uStudios' in tables):
create_tables(conn, table = 'uStudios')
if not ('uHalls' in tables):
create_tables(conn, table = 'uHalls')
if not ('uBooking_parsing' in tables):
create_tables(conn, table = 'uBooking_parsing')
if not ('uBooking' in tables):
create_tables(conn, table = 'uBooking')
elif answer != 'n':
print('Error in input!')
return list()
conn.commit()
. :
conn.commit()
studios = studio_list()
new_studios = studios[[x not in list(db_to_studios(conn).index) for x in list(studios.index)]]
if len(new_studios) > 0:
print(str(len(new_studios)) + ' new studios detected: \n' + str(list(new_studios['name'])))
studios_to_db(conn, new_studios)conn.commit()
:
halls = hall_list(list(studios.index)).sort_index()
new_halls = halls[[x not in list(db_to_halls(conn).index) for x in list(halls.index)]]
if len(new_halls) > 0:
halls_to_db(conn, new_halls)
conn.commit()
uBooking_parsing. , .. booking_to_db
booking_to_db(conn, halls.index)
conn.commit()
uBooking. uBooking uBooking_parsing ( , ) :
cur.execute('DELETE FROM uBooking')
cur.execute('''
insert into uBooking (hall_id, date, hour, is_working_hour, min_hours, price, is_booked, duration, parsing_date)
select hall_id, date, hour, is_working_hour, min_hours, price, is_booked, duration, parsing_date
from
(
select *, row_number() over(partition by hall_id, date, hour order by parsing_date desc) rn
from uBooking_parsing
) t
where rn = 1
''')
conn.commit()
:
update_open_dates(conn)
conn.commit() conn.close()将数据保存到数据库的解析已成功配置!
我们通过以下过程启动解析/更新:
update_parsing()结果
在上一篇和上一篇文章中,我们研究了用于解析照相馆开放信息的算法。获得的数据收集在数据库中。
在接下来的文章中,我们将考虑分析所获得的数据的例子。
您可以在我的github页面上找到完成的项目。