哈Ha!我请您注意Jaime Sevilla 撰写的文章“在TensorFlow + Keras中实现RoI池化”的翻译。
我目前正在参加机器学习课程。在“计算机视觉”培训模块中,有必要研究RoI层的合并。以下文章对我来说似乎很有趣,因此我决定与社区分享翻译。
在这篇文章中,我们将解释RoI池(关注区域)的基本概念和一般用法,并提供使用TensorFlow Keras层的实现。
这篇文章的目标读者是熟悉(卷积)神经网络(CNN)基本理论并且能够使用Keras构建和运行简单模型的人。
如果您只是在这里获取代码,请在此处查看,不要忘记喜欢并分享该文章!
了解RoI池
RoI Pooling由Ross Girshik在Fast R-CNN文章中提出,作为其对象识别管道的一部分。
在RoI Pooling的一般用例中,我们有一个图像对象,并通过边界框指定了几个感兴趣的区域(RoI)。我们想从每个RoI创建嵌入(嵌入-将任意实体(一张图片)映射到某个矢量)。
例如,在R-CNN设置中,我们有一张图像和一个候选区域突出显示引擎,该引擎为图像的潜在有趣部分创建了边界框。现在,我们要为图像的每个建议部分创建一个嵌入。
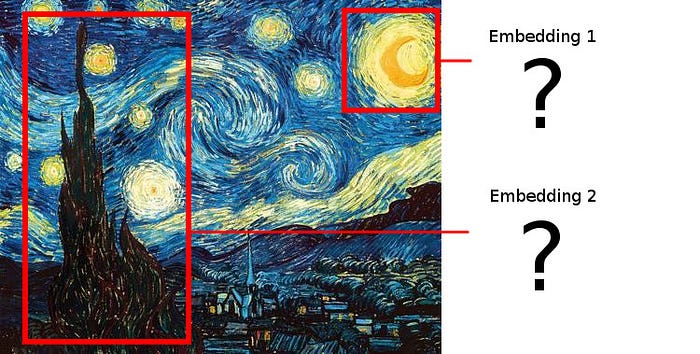
简单地裁剪每个建议的区域将不起作用,因为我们希望将生成的嵌入彼此叠加,并且建议的区域不一定具有相同的形状!
, . ?
- (pooling).
max pooling, ( ) , , .

maxpool
, – : .
. RoI ?

ROI Pooling , pooling.
, ROI Pooling.
RoI Pooling.
RoI Pooling — . , RoI, . , .
-, ( RoI Pooling ), ( ), (end-to-end) (single-pass) .
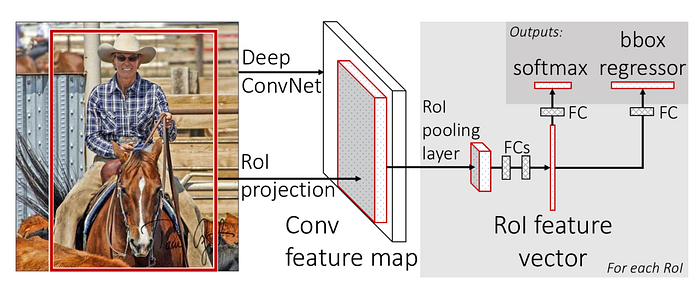
Fast R-CNN, RoI Pooling,
, R-CNN , (RoI). RoI Pooling CNN . .
-, -, RoI Pooling (visual attention).
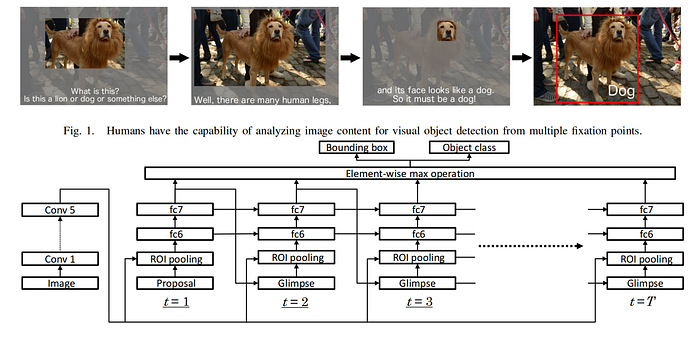
Attentional Network , ROI Pooling, Hara ..
Attentional Network , Hara attention, ROI ROI Pooling. (t = 1), ROI Pooling (Fully Connected). Glimpse () (t = 2) , ROI Pooling. .
.
, , ROI.
:
- (batch) . , . (batch_size, img_width, img_height, n_channels), batch_size- , img_width — , img_height — , n_channels — .
- (batch) ROI. , - . 4 , (batch_size, n_rois, 4), batch_size — ROI, n_rois — ROI.
:
- , ROI. (batch_size, n_rois, pooled_width, pooled_height, n_channels). batch_size- , n_rois — ROI, pooled_width — , pooled_height— , n_channels — .
Keras
Keras Layer.
tf.keras init, build call . , build , , . compute_output_shape.
, .
def __init__(self, pooled_height, pooled_width, **kwargs):
self.pooled_height = pooled_height
self.pooled_width = pooled_width
super(ROIPoolingLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs). , . .
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
""" Returns the shape of the ROI Layer output
"""
feature_map_shape, rois_shape = input_shape
assert feature_map_shape[0] == rois_shape[0]
batch_size = feature_map_shape[0]
n_rois = rois_shape[1]
n_channels = feature_map_shape[3]
return (batch_size, n_rois, self.pooled_height,
self.pooled_width, n_channels)compute_output_shape — , , .
(call). — , . , ROI Pooling, .
, , ROI .
.
@staticmethod
def _pool_roi(feature_map, roi, pooled_height, pooled_width):
""" Applies ROI Pooling to a single image and a single ROI
"""# Compute the region of interest
feature_map_height = int(feature_map.shape[0])
feature_map_width = int(feature_map.shape[1])
h_start = tf.cast(feature_map_height * roi[0], 'int32')
w_start = tf.cast(feature_map_width * roi[1], 'int32')
h_end = tf.cast(feature_map_height * roi[2], 'int32')
w_end = tf.cast(feature_map_width * roi[3], 'int32')
region = feature_map[h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end, :]
..., .
, ROI , 0 1. , ROI 4- , (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max ).
ROI , , , : , , ROI Pooling, , , ROI.
, TensorFlow.
...
# Divide the region into non overlapping areas
region_height = h_end - h_start
region_width = w_end - w_start
h_step = tf.cast(region_height / pooled_height, 'int32')
w_step = tf.cast(region_width / pooled_width , 'int32')
areas = [[(
i*h_step,
j*w_step,
(i+1)*h_step if i+1 < pooled_height else region_height,
(j+1)*w_step if j+1 < pooled_width else region_width
)
for j in range(pooled_width)]
for i in range(pooled_height)]
...ROI, .
2D , , , .
, , , , ROI (region_height // pooled_height, region_width // pooled_width), ROI, .
2D , .
...
# Take the maximum of each area and stack the result
def pool_area(x):
return tf.math.reduce_max(region[x[0]:x[2],x[1]:x[3],:], axis=[0,1])
pooled_features = tf.stack([[pool_area(x) for x in row] for row in areas])
return pooled_features . pool_area, , , , , .
pool_area , , list comprehension .
(pooled_height, pooled_width, n_channels), RoI .
— RoI . tf.map_fn (n_rois, pooled_height, pooled_width, n_channels).
@staticmethod
def _pool_rois(feature_map, rois, pooled_height, pooled_width):
""" Applies ROI pooling for a single image and varios ROIs
"""
def curried_pool_roi(roi):
return ROIPoolingLayer._pool_roi(feature_map, roi,
pooled_height, pooled_width)
pooled_areas = tf.map_fn(curried_pool_roi, rois, dtype=tf.float32)
return pooled_areas, . tf.map_fn (, x), , .
def call(self, x):
""" Maps the input tensor of the ROI layer to its output
"""
def curried_pool_rois(x):
return ROIPoolingLayer._pool_rois(x[0], x[1],
self.pooled_height,
self.pooled_width)
pooled_areas = tf.map_fn(curried_pool_rois, x, dtype=tf.float32)
return pooled_areas, dtype tf.map_fn , . , , , Tensorflow.
:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Layer
class ROIPoolingLayer(Layer):
""" Implements Region Of Interest Max Pooling
for channel-first images and relative bounding box coordinates
# Constructor parameters
pooled_height, pooled_width (int) --
specify height and width of layer outputs
Shape of inputs
[(batch_size, pooled_height, pooled_width, n_channels),
(batch_size, num_rois, 4)]
Shape of output
(batch_size, num_rois, pooled_height, pooled_width, n_channels)
"""
def __init__(self, pooled_height, pooled_width, **kwargs):
self.pooled_height = pooled_height
self.pooled_width = pooled_width
super(ROIPoolingLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
""" Returns the shape of the ROI Layer output
"""
feature_map_shape, rois_shape = input_shape
assert feature_map_shape[0] == rois_shape[0]
batch_size = feature_map_shape[0]
n_rois = rois_shape[1]
n_channels = feature_map_shape[3]
return (batch_size, n_rois, self.pooled_height,
self.pooled_width, n_channels)
def call(self, x):
""" Maps the input tensor of the ROI layer to its output
# Parameters
x[0] -- Convolutional feature map tensor,
shape (batch_size, pooled_height, pooled_width, n_channels)
x[1] -- Tensor of region of interests from candidate bounding boxes,
shape (batch_size, num_rois, 4)
Each region of interest is defined by four relative
coordinates (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) between 0 and 1
# Output
pooled_areas -- Tensor with the pooled region of interest, shape
(batch_size, num_rois, pooled_height, pooled_width, n_channels)
"""
def curried_pool_rois(x):
return ROIPoolingLayer._pool_rois(x[0], x[1],
self.pooled_height,
self.pooled_width)
pooled_areas = tf.map_fn(curried_pool_rois, x, dtype=tf.float32)
return pooled_areas
@staticmethod
def _pool_rois(feature_map, rois, pooled_height, pooled_width):
""" Applies ROI pooling for a single image and varios ROIs
"""
def curried_pool_roi(roi):
return ROIPoolingLayer._pool_roi(feature_map, roi,
pooled_height, pooled_width)
pooled_areas = tf.map_fn(curried_pool_roi, rois, dtype=tf.float32)
return pooled_areas
@staticmethod
def _pool_roi(feature_map, roi, pooled_height, pooled_width):
""" Applies ROI pooling to a single image and a single region of interest
"""
# Compute the region of interest
feature_map_height = int(feature_map.shape[0])
feature_map_width = int(feature_map.shape[1])
h_start = tf.cast(feature_map_height * roi[0], 'int32')
w_start = tf.cast(feature_map_width * roi[1], 'int32')
h_end = tf.cast(feature_map_height * roi[2], 'int32')
w_end = tf.cast(feature_map_width * roi[3], 'int32')
region = feature_map[h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end, :]
# Divide the region into non overlapping areas
region_height = h_end - h_start
region_width = w_end - w_start
h_step = tf.cast( region_height / pooled_height, 'int32')
w_step = tf.cast( region_width / pooled_width , 'int32')
areas = [[(
i*h_step,
j*w_step,
(i+1)*h_step if i+1 < pooled_height else region_height,
(j+1)*w_step if j+1 < pooled_width else region_width
)
for j in range(pooled_width)]
for i in range(pooled_height)]
# take the maximum of each area and stack the result
def pool_area(x):
return tf.math.reduce_max(region[x[0]:x[2], x[1]:x[3], :], axis=[0,1])
pooled_features = tf.stack([[pool_area(x) for x in row] for row in areas])
return pooled_features! , 1- 100x200, 2 RoI, 7x3. , 4 . — 1, 50 (-1, -3).
import numpy as np# Define parameters
batch_size = 1
img_height = 200
img_width = 100
n_channels = 1
n_rois = 2
pooled_height = 3
pooled_width = 7# Create feature map input
feature_maps_shape = (batch_size, img_height, img_width, n_channels)
feature_maps_tf = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=feature_maps_shape)
feature_maps_np = np.ones(feature_maps_tf.shape, dtype='float32')
feature_maps_np[0, img_height-1, img_width-3, 0] = 50
print(f"feature_maps_np.shape = {feature_maps_np.shape}")# Create batch size
roiss_tf = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, n_rois, 4))
roiss_np = np.asarray([[[0.5,0.2,0.7,0.4], [0.0,0.0,1.0,1.0]]], dtype='float32')
print(f"roiss_np.shape = {roiss_np.shape}")# Create layer
roi_layer = ROIPoolingLayer(pooled_height, pooled_width)
pooled_features = roi_layer([feature_maps_tf, roiss_tf])
print(f"output shape of layer call = {pooled_features.shape}")# Run tensorflow session
with tf.Session() as session:
result = session.run(pooled_features,
feed_dict={feature_maps_tf:feature_maps_np,
roiss_tf:roiss_np})
print(f"result.shape = {result.shape}")
print(f"first roi embedding=\n{result[0,0,:,:,0]}")
print(f"second roi embedding=\n{result[0,1,:,:,0]}"), TensorFlow, .
:
feature_maps_np.shape = (1, 200, 100, 1)
roiss_np.shape = (1, 2, 4)
output shape of layer call = (1, 2, 3, 7, 1)
result.shape = (1, 2, 3, 7, 1)
first roi embedding=
[[1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
second roi embedding=
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 50.]], . — 1, , 50.
, !
, !
, ROI Pooling (attention). , , Keras , ROI Pooling .
, , , !
Ari Brill, Tjark Miener Bryan Kim .
- Ross Girshick. Fast R-CNN. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2015.
- Kota Hara, Ming-Yu Liu, Oncel Tuzel, Amir-massoud Farahmand. Attentional Network for Visual Object Detection. 2017.